fanbeam
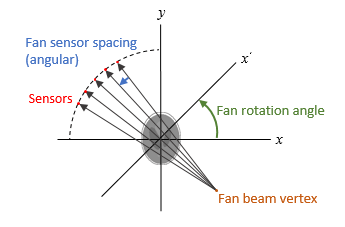
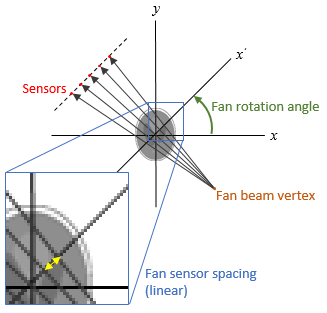
Fan-beam transform
Description
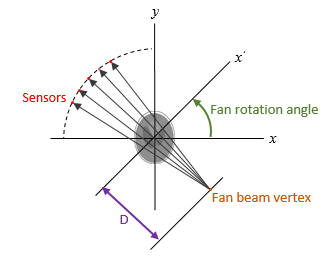
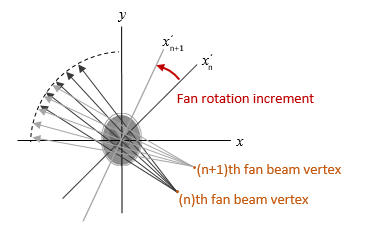
F = fanbeam(I,D,Name,Value)
[
also returns the location of fan-beam sensors in
F,fanSensorPos,fanRotAngles]
= fanbeam(___)fanSensorPos and the rotation angles
where the fan-beam projections are calculated in
fanRotAngles.
Examples
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Tips
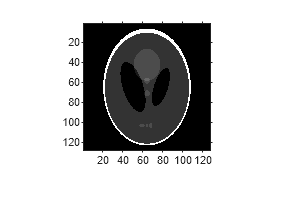
As a guideline, try making D a few pixels larger than
half the image diagonal dimension, calculated as follows.
sqrt(size(I,1)^2 + size(I,2)^2)
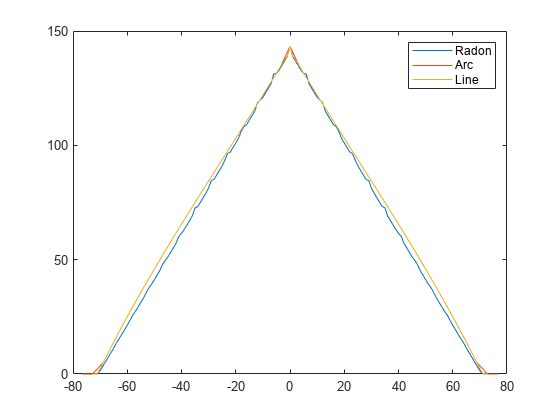
The values returned in F are a numerical approximation of
the fan-beam projections. The algorithm depends on the Radon transform,
interpolated to the fan-beam geometry. The results vary depending on the
parameters used. You can expect more accurate results when the image is
larger, D is larger, and for points closer to the
middle of the image, away from the edges.
References
[1] . pp. 92-93.
Version History
Introduced before R2006a