Wind Turbine Induction Generator (Phasor Type)
Implement phasor model of squirrel-cage induction generator driven by variable pitch wind turbine
Libraries:
Simscape /
Electrical /
Specialized Power Systems /
Electrical Machines
Description
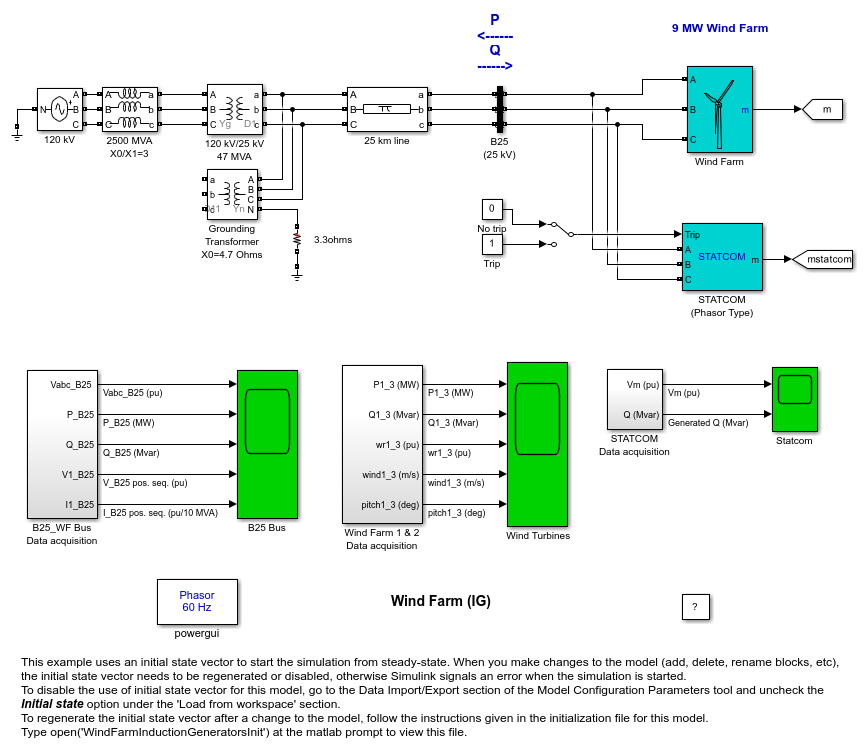
The wind turbine and the induction generator (WTIG) are shown below. The stator winding is connected directly to the grid and the rotor is driven by the wind turbine. The power captured by the wind turbine is converted into electrical power by the induction generator and is transmitted to the grid by the stator winding. The pitch angle is controlled in order to limit the generator output power to its nominal value for high wind speeds. In order to generate power the induction generator speed must be slightly above the synchronous speed. But the speed variation is typically so small that the WTIG is considered to be a fixed-speed wind generator. The reactive power absorbed by the induction generator is provided by the grid or by some devices like capacitor banks, SVC, STATCOM, or synchronous condenser.

Pitch Angle Control System
The wind turbine model uses the Wind Turbine block of the Renewables/Wind Generation library. See documentation of this block for details.
A Proportional-Integral (PI) controller is used to control the blade pitch angle in
order to limit the electric output power to the nominal mechanical power. The pitch angle is
kept constant at zero degrees when the measured electric output power is under its nominal
value. When it increases above its nominal value, the PI controller increases the pitch
angle to bring back the measured power to its nominal value. The control system is
illustrated in the figure below:
Examples
Ports
Input
Output
Conserving
Parameters
References
[1] Siegfried Heier, “Grid Integration of Wind Energy Conversion Systems,” John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 1998, ISBN 0-471-97143-X
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2006a