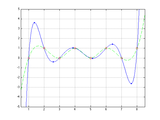
Lagrange Interpolator Polynomial
The two inputs X and Y are vectors defining a set of N points. The function uses Lagrange's method to find the N-1th order polynomial that passes through all these points, and returns in P the N coefficients defining that polynomial. Then, polyval(P,X) = Y.
R returns the x co-ordinates of the N-1 extrema/inflection points of the resulting polynomial (roots of its derivative), and S returns the value of the polynomial at those points.
For a general-purpose way to find a smooth curve connecting points, you probably want to use SPLINE instead.
Cite As
Dan Ellis (2026). Lagrange Interpolator Polynomial (https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/13151-lagrange-interpolator-polynomial), MATLAB Central File Exchange. Retrieved .
MATLAB Release Compatibility
Platform Compatibility
Windows macOS LinuxCategories
- AI and Statistics > Curve Fitting Toolbox > Interpolation >
- MATLAB > Mathematics > Elementary Math > Polynomials >
Tags
Acknowledgements
Inspired by: Lagrange polynomial interpolation, lagrange interpolation and derivative
Discover Live Editor
Create scripts with code, output, and formatted text in a single executable document.
lagrangepoly/
lagrangepoly/html/
| Version | Published | Release Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0.0.0 | - added example to comments as per code metrics report
|