NEURON toolbox for MATLAB
⚠️ This toolbox has specific requirements depending on operating system
- Windows: Matlab R2022a or higher, MinGW compiler, and Administrator rights
- Linux: Matlab R2023a or higher and GCC compiler
- Mac: [Under Development] Matlab R2023a or higher, Intel Macs only and Clang compiler
For the compiler used, the version should preferably match the exact version used to compile NEURON, as using a newer or older version could have different symbol name-mangling.
The NEURON Toolbox provides a MATLAB API to NEURON, using the MATLAB provided clibgen and clib packages to connect MATLAB and NEURON.
The NEURON simulation environment is used in laboratories and classrooms around the world for building and using computational models of neurons and networks of neurons.
About this toolbox:
- The +neuron package defines the MATLAB API to NEURON. All calls to NEURON from MATLAB should only use methods and properties exposed by the classes in this package and should not directly use clib.neuron. This is because the +neuron package takes care of proper initialization of NEURON, and correct cleanup of NEURON objects.
- With clib, the NEURON shared library can be used through the clibgen
generated wrapper interface. The functions and variables exposed in the
wrapper interface can be used directly from MATLAB, e.g. it is possible
to call the NEURON function nrn_sec_pop from MATLAB with
clib.neuron.nrn_sec_pop(). - With clibgen a MATLAB interface to the NEURON library is built. This
results in a wrapper shared library. Prebuilt wrappers for certain
Operating System and Compiler combinations may be provided.
- To generate the interface, the underlying library should preferably expose an API in a header file. Since NEURON itself does not provide a C or C++ API that is directly useable in clibgen, the MATLAB-NEURON project also contains header and C++ files that define a C++ API, containing the NEURON functionality that needs to be available from MATLAB.
MATLAB is a registered trademark of The MathWorks, Inc.
For more detailed technical information about e.g. code structure, see doc/DEV_README.md.
Before using the toolbox for the first time, go through the first time only steps. On Windows, these steps need to be run from a Matlab session with Administrator rights.
Linux and Mac: To be able to use the toolbox, Matlab always needs to be started from an environment with specific environment variables, see first time only for details. Also, output printed from within NEURON itself will show in the shell from which Matlab is started, instead of the Matlab command window.
In each Matlab session where you want to use the toolbox, run the script setup.m. Alternatively, add a call to this setup.m in your startup.m file.
A comprehensive example live script, encompassing the smaller examples and providing additional explanation, can be found at examples/example_livescript.mlx.
Smaller example scripts are available at:
-
examples/example_run.m
- to initialize a Neuron session and call some top-level functions from the library
-
examples/example_vector.m
- to create a Vector object and calculate some properties
-
examples/example_morph.m
- to generate a morphology by connecting different Sections, and add 3D points to them
-
examples/example_crash.m
- to cause a ⚠️ crash by causing a method with the wrong arguments
-
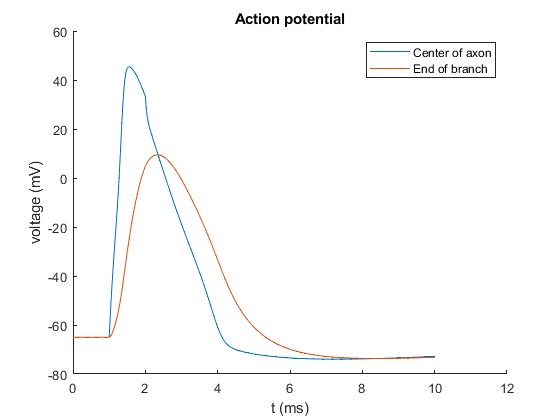
examples/example_acpot.m
- to generate an action potential
example_acpot should result in:
The main Neuron class can be found at neuron.Session. A (singleton)
neuron.Session is returned upon calling the neuron.launch() function.
n = neuron.launch();Now all top-level variables, functions and classes can be accessed using this object. The available variables, functions and classes, as well as their Neuron types can be displayed with:
n.list_functions();Top-level variables, functions and objects can be called directly. E.g.:
disp(n.t); % Display the time
n.fadvance(); % Advance by one timestep
v = n.Vector(); % Create a Vector objectIf you create an object like a Vector, you can see a list of its properties and methods with:
v.list_methods();Run the tests with:
runtests +testsA non-exhaustive list:
-
size(vector)returns an array[1 N]withN == length(vector), as is customary in MATLAB. In Python,size(vector)is a scalar. - When iterating over segments we use
section.segments(), which returns a cell array with Segment objects. In Python, we can simply writefor segment in section. - Call chaining is not (yet) always available in MATLAB. As such, we cannot
use
t = n.Vector().record(ref);; instead we have to writet = n.Vector(); t.record(ref);. This is due to the way dynamic function calls are setup withsubsref.
Here the steps are given that need to be done only once to be able to use the toolbox.
- Make sure NEURON is installed (see http://neuron.yale.edu/).
- Linux and Mac: start Matlab from a bash shell with the correct PATH, HOC_LIBRARY_PATH and on Linux LD_LIBRARY_PATH, on Mac DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH. Matlab always needs to be started from such a shell, not just the first time only.
- Get the directory where libnrniv is installed, within the NEURON installation folder
- Get the directory where this toolbox is installed
- Determine the value of matlabroot (https://nl.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/matlabroot.html)
- Use these values to set the HOC_LIBRARY_PATH and LD_LIBRARY_PATH / DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH. Example shell scripts are available for Linux and Mac. Within these scripts, replace
<..matlabroot..>,<..neuron-directory..>and<..matlabneuroninterface..>with the correct directory paths. - Depending on how Neuron was installed, it may be that also the PATH variable needs to be updated. See item 6 'Check it works'.
- Make sure to setup your MEX C++ compiler; for more information about this, run
mex -setup cppin MATLAB.- Windows: MinGW-w64
- Linux: gcc
- Mac: clang
- Update neuron_lib_directory in +utils/Paths.m if needed.
- Run the MATLAB scripts in the following order:
-
setup
- This script needs to be run every time a new MATLAB session is started
- It adds the appropriate directories to your path
-
utils.build_interface
- This script needs to be run once to generate the library interface, and only needs to be re-run if the interface changes (for example when using a newer Neuron version)
- It builds the library interface (neuron/neuronInterface.*)
- Please note: on Windows you need administrator rights to run build_interface
-
setup
- Check it works:
- With the previous steps completed, run the matlab scripts example_run and example_acpot to check that the matlabneuroninterface works.
- Linux and Mac, additionally:
- Run example_loadfile to check that the HOC_LIBRARY_PATH has been set correctly.
- Run example_mod to check that the PATH is correct. If this example fails, update the PATH per the instructions in the example startup script.
Cite As
Robert McDougal (2024). NEURON toolbox for MATLAB (https://github.com/mcdougallab/matlabneuroninterface/releases/tag/v0.0.1), GitHub. Retrieved .
MATLAB Release Compatibility
Platform Compatibility
Windows macOS LinuxCategories
Tags
Community Treasure Hunt
Find the treasures in MATLAB Central and discover how the community can help you!
Start Hunting!Discover Live Editor
Create scripts with code, output, and formatted text in a single executable document.
+neuron
+neuron/+stack
+tests
+utils
examples/basic_functionality
examples/input
examples/morphology
examples/plotting
examples/simulation
examples
| Version | Published | Release Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0.1 |