IbIPP
IbIPP
IbIPP which stands for Image-based Initialization and Post-Processing
is an open-source code for initializing and post-processing free-form 2D topology optimization problems.
Syntax
-
ibipp(file, nelx, volfrac) Performs topology optimization on the image provided in file using the number of elements in the x-direction nelx, the required volume fraction volfrac, and other default parameters.
-
ibipp(file, nelx, volfrac,fmag,fang) Performs topology optimization using file, nelx, volfrac, vectors of force magnitudes fmag, and force angles fang, and other default parameters.
-
ibipp(...,'PropertyName',VALUE,'PropertyName',VALUE,...) performs topology optimization using the following property values:
Table 1: Name-value inputs
| Name-value | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| pressure | Pressure loads (multiple loads must be in a vector) | |
| optimization | Type of topology optimization approach | Density, BESO, Level Set, SEMDOT |
| densityType | Type of density-based method | SIMP, RAMP |
| preserveSupport | Preserve elements within the support region in the image | 0 – none |
| 1 – Only completely fixed elements | ||
| 2 – Only elements fixed in the x-axis | ||
| 3 – Only elements fixed in the y-axis | ||
| 4 – the union of 1 and 2 | ||
| 5 – the union of 1 and 3 | ||
| 6 - the union of 2 and 3 | ||
| 7 – the union of 1, 2, and 3 | ||
| preserveLoad | Preserve elements within the load region in the image | 0 – none |
| 1 – elements in the force region | ||
| 2 – elements in the pressure region | ||
| 3 – the union of 1 and 2 | ||
| filterRadius | Specify filter radius for density-based and BESO approaches | >1 |
| filter | Specify filter type for density-based approaches | 1 – density |
| 2 – sensitivity | ||
| 3 - Heaviside projection | ||
| beta | Regularization parameter for Heaviside projection | >1 |
| penaltySIMP | Penalty value for SIMP density-based approach | >1 |
| penaltyRAMP | Penalization factor for RAMP density-based approach | >1 |
| ER | Evolution ratio for BESO | >0 |
| tau | Regularization parameter for level set method (reaction diffusion) | >0 |
| YoungsModulus | Youngs Modulus material property | >1 |
| PoissonRatio | Poisson Ratio material property | >0 |
| modelName | Name given to model obtained by extrusion or revolution of the optimized topology. Must end in .stl | |
| modelType | Modeling by extrusion or revolution | Extrude or revolve |
| extrudeLength | Length for extrusion - a factor multiplied by min(nelx,nely) to obtain the length of the 3rd dimension | >0 |
| symmetry | Specifies the position of the line of symmetry for symmetry-based modeling | None, Left, bottom, right, and top |
| distancetoaxis | Distance between the optimized topology and its revolution axis to the left for revolution-based modeling | ≥0 |
| revolutionAngle | The angle of revolution for revolution-based modeling | ≥0 |
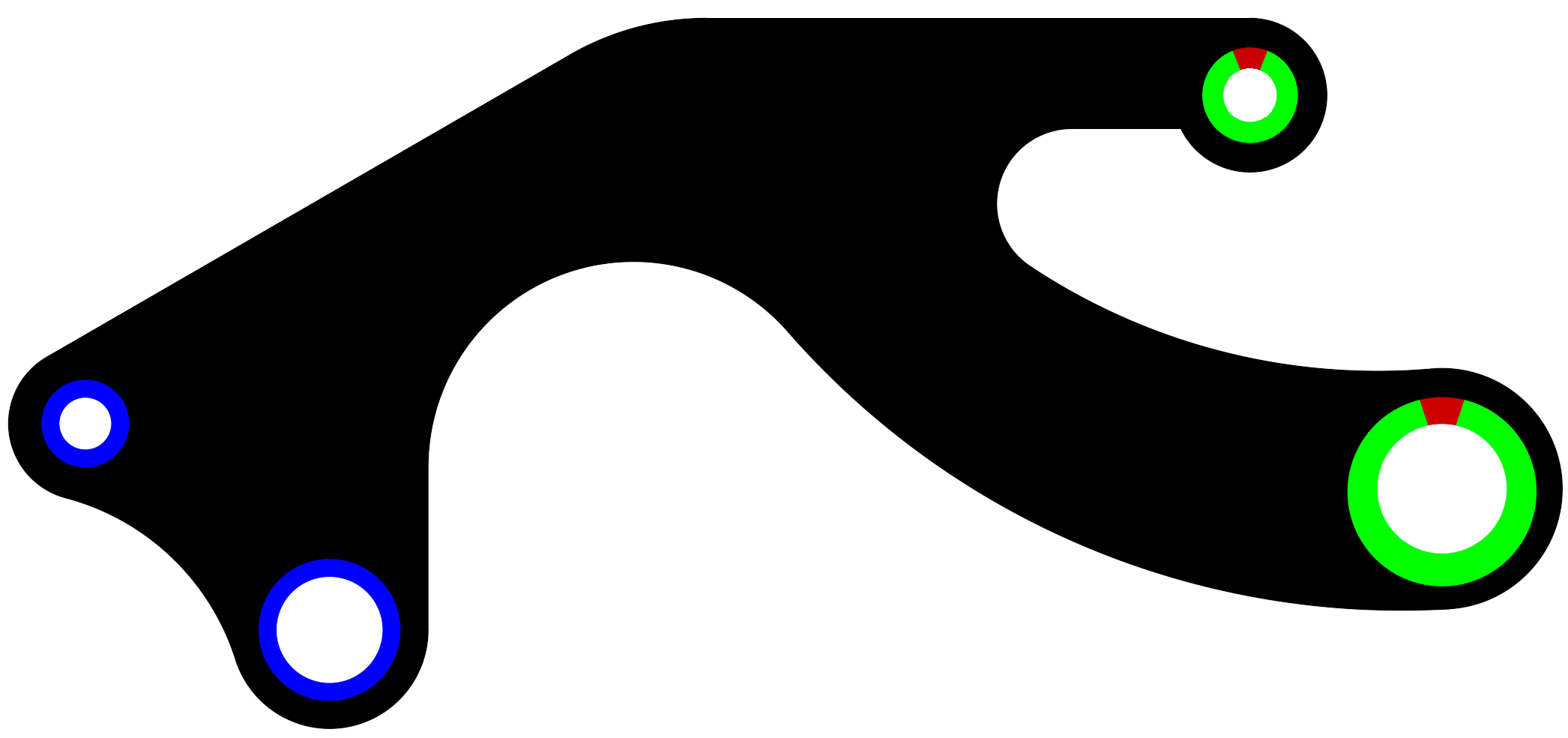
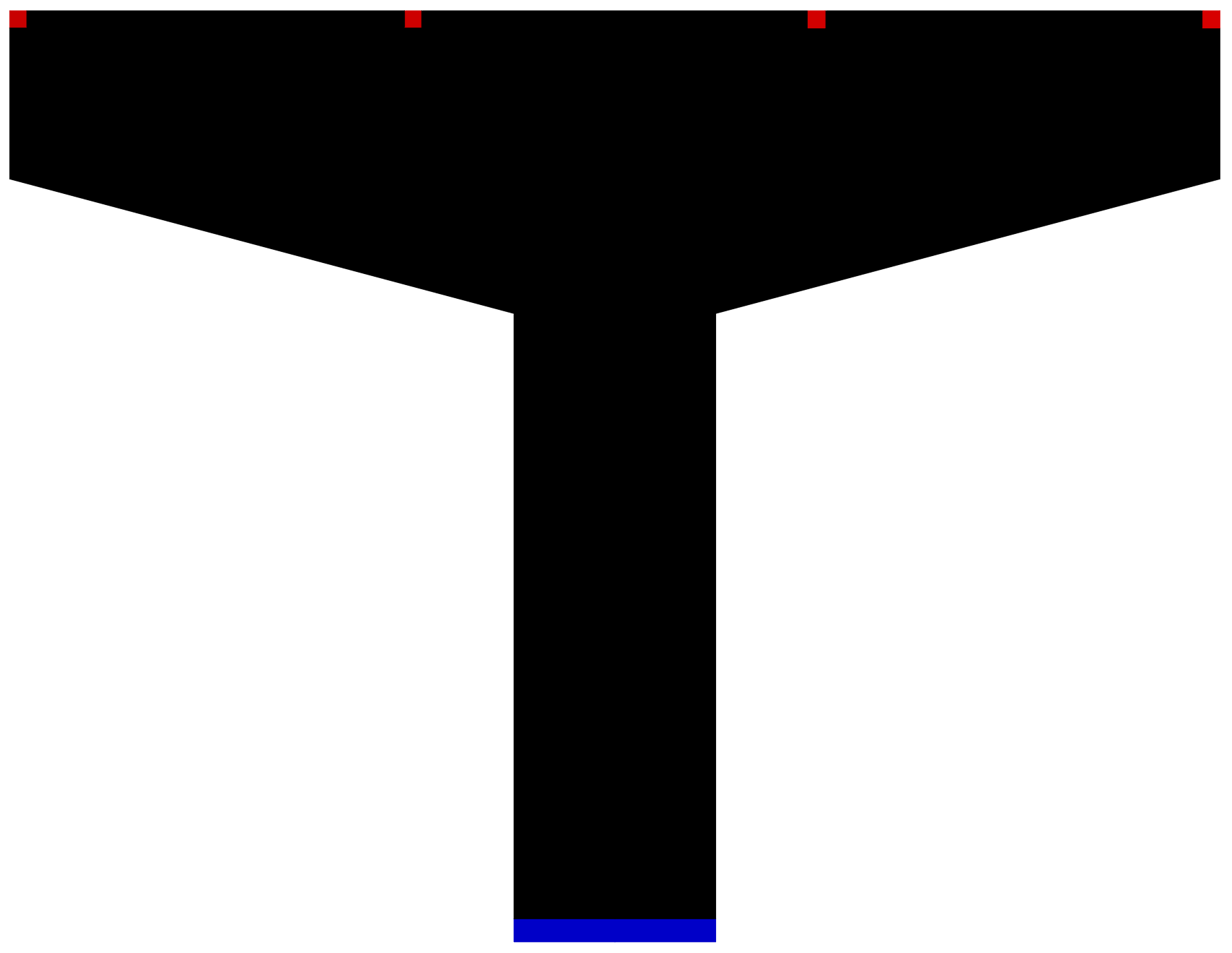
Table 2: Color codes (RGB) for creating an input image file
| Features | Color code rules | Recommended values |
|---|---|---|
| Designable domain | R∩G∩B<200 | 0 0 0 |
| Non-designable domain | R∩G∩B>200 | 255 255 255 |
| Point load | 200≤R≤255, G=0, B=0 | 200 0 0 |
| Pressure | 200≤R≤230, 100≤G≤150, B=0 | 200 100 0 |
| Preserved region | R=0, 200≤G≤255, B=0 | 0 200 0 |
| Fixed region | R=0, G=0, 200≤B≤255 | 0 0 200 |
| Region fixed along x | 100≤R≤150, G=0, 200≤B≤255 | 100 0 200 |
| Region fixed along y | R=0, 200≤G≤255, 200≤B≤255 | 0 200 200 |
- Note: for multiple forces or pressure, R should be in multiples of 5 starting from 200 for forces (200, 205, 210,...etc) and G should be in multiples of 5 starting from 100 for pressures (100, 105, 110,..etc)
Examples:
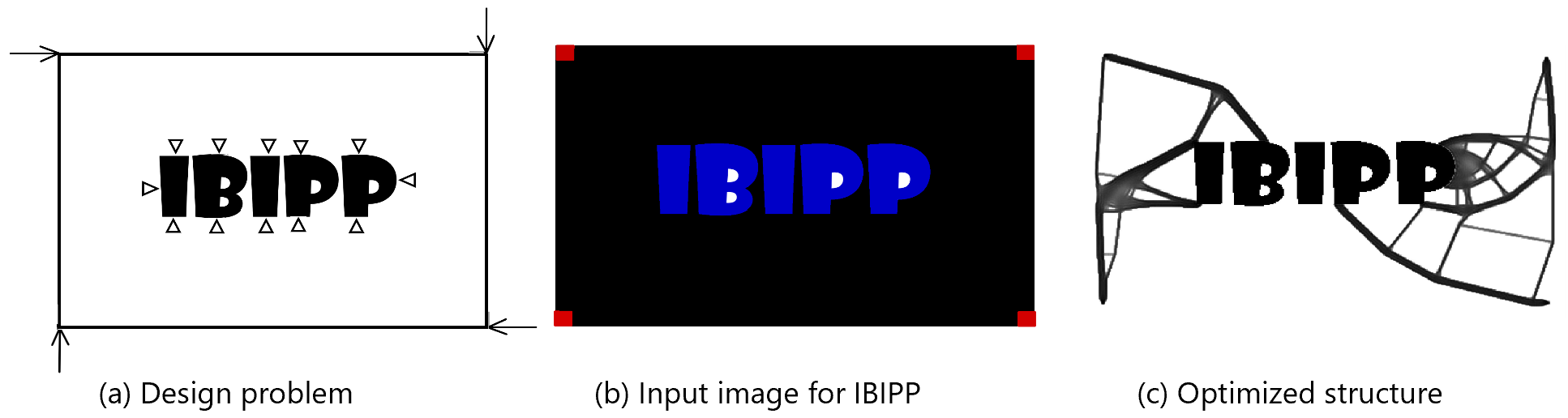
The following examples show how ibipp can be used. Images of some sample design problems and their corresponding input images for ibipp have been prepared and are in this repository. When developing an input image for a design problem, Table 2 should be used while Table 1 outlines the possible name-value inputs. Any image tool can be used to prepare the input file but .png is the preferred file extension.
-
Example 1: Optimize a half-MBB using default values of optional inputs
- ibipp('Example_pics\half_mbb.png',150,0.4)
-
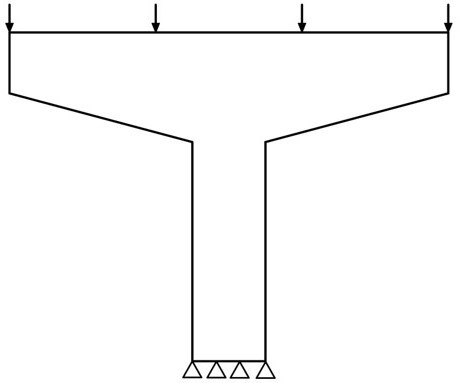
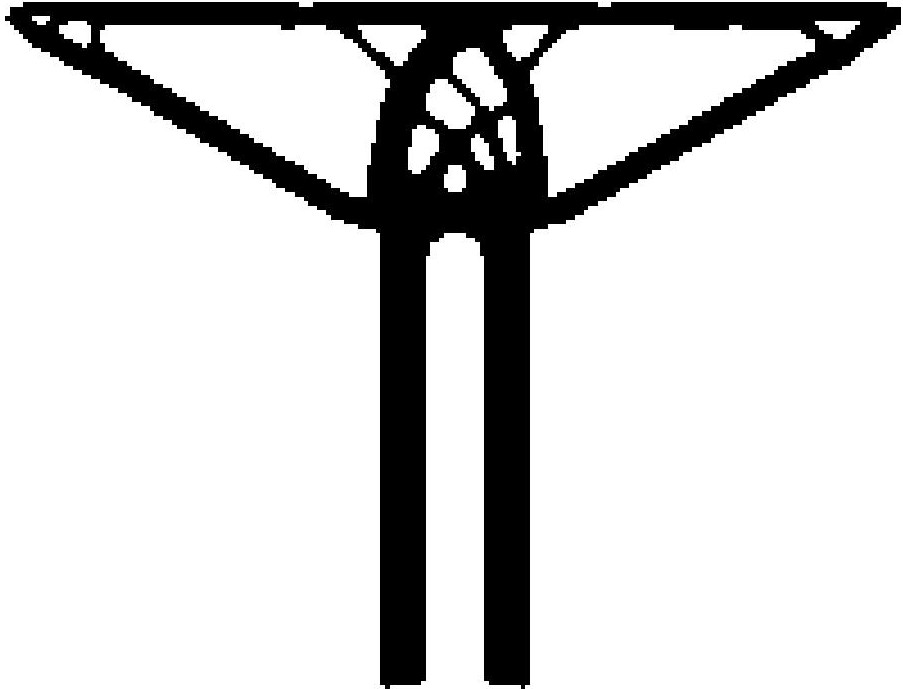
Example 2: Optimize a Hammerhead pier using the BESO approach
- ibipp('Example_pics\hammerhead.png',200,0.5,[2 1 1 2],[180 180 180 180],'optimization','BESO','filterRadius',3)
-
Example 3: Optimize a 2-point loading mechanical part while preserving load and support elements
- ibipp('Example_pics\2point.png',300,0.45,[1 1],[0 0],'optimization','levelset','tau',5e-5,'preserveLoad',1,'preserveSupport',1)
-
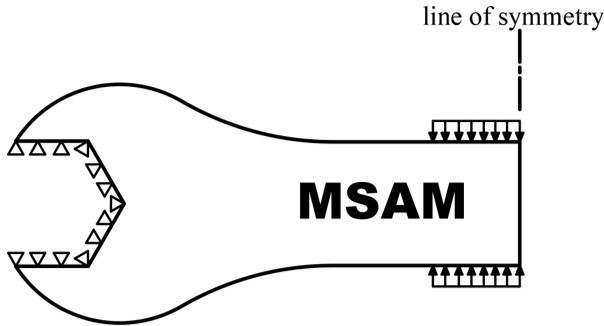
Example 4: Optimize a half-spanner design and generate an extruded full spanner STL model
- ibipp('Example_pics\half_spanner.png',250,0.5,'pressure',[1,1],'preserveload',2,'preservesupport',1,'modelname','spanner.stl','symmetry','right','modeltype','extrude','extrudelength',0.2)
Supporting Open-Source Codes
IBIPP utilizes other open-source codes such as top88.m by Andreassen et.al, esoL.m by Xia et. al., levelset88.m by Otomori et.al, revolve2D.m by Treeby and Cox, and stlwrite.m by Sven.
To Cite
If you find this code helpful in your work, please cite this open access paper
Cite As
Osezua (2026). IbIPP (https://github.com/CADmaniac/IbIPP/releases/tag/v1.0), GitHub. Retrieved .
MATLAB Release Compatibility
Platform Compatibility
Windows macOS LinuxTags
Community Treasure Hunt
Find the treasures in MATLAB Central and discover how the community can help you!
Start Hunting!Discover Live Editor
Create scripts with code, output, and formatted text in a single executable document.
| Version | Published | Release Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 |