Texture Segmentation Using Texture Filters
This example shows how to identify and segment regions based on their texture.
Read Image
Read and display a grayscale image of textured patterns on a bag.
I = imread('bag.png'); imshow(I) title('Original Image')

Create Texture Image
Use entropyfilt to create a texture image. The function entropyfilt returns an array where each output pixel contains the entropy value of the 9-by-9 neighborhood around the corresponding pixel in the input image I. Entropy is a statistical measure of randomness.
You can also use stdfilt and rangefilt to achieve similar segmentation results. For comparison to the texture image of local entropy, create texture images S and R showing the local standard deviation and local range, respectively.
E = entropyfilt(I); S = stdfilt(I,ones(9)); R = rangefilt(I,ones(9));
Use rescale to rescale the texture images E and S so that pixel values are in the range [0, 1] as expected of images of data type double.
Eim = rescale(E); Sim = rescale(S);
Display the three texture images in a montage.
montage({Eim,Sim,R},'Size',[1 3],'BackgroundColor','w',"BorderSize",20)
title('Texture Images Showing Local Entropy, Local Standard Deviation, and Local Range')
Create Mask for Bottom Texture
This example continues by processing the entropy texture image Eim. You can repeat a similar process for the other two types of texture images with other morphological functions to achieve similar segmentation results.
Threshold the rescaled image Eim to segment the textures. A threshold value of 0.8 is selected because it is roughly the intensity value of pixels along the boundary between the textures.
BW1 = imbinarize(Eim,0.8);
imshow(BW1)
title('Thresholded Texture Image')
The segmented objects in the binary image BW1 are white. If you compare BW1 to I, you notice the top texture is overly segmented (multiple white objects) and the bottom texture is segmented almost in its entirety. Remove the objects in the top texture by using bwareaopen.
BWao = bwareaopen(BW1,2000);
imshow(BWao)
title('Area-Opened Texture Image')
Use imclose to smooth the edges and to close any open holes in the object in BWao. Specify the same 9-by-9 neighborhood that was used by entropyfilt.
nhood = ones(9);
closeBWao = imclose(BWao,nhood);
imshow(closeBWao)
title('Closed Texture Image')
Use imfill to fill holes in the object in closeBWao. The mask for the bottom texture is not perfect because the mask does not extend to the bottom of the image. However, you can use the mask to segment the textures.
mask = imfill(closeBWao,'holes'); imshow(mask); title('Mask of Bottom Texture')

Use Mask to Segment Textures
Separate the textures into two different images.
textureTop = I;
textureTop(mask) = 0;
textureBottom = I;
textureBottom(~mask) = 0;
montage({textureTop,textureBottom},'Size',[1 2],'BackgroundColor','w',"BorderSize",20)
title('Segmented Top Texture (Left) and Segmented Bottom Texture (Right)')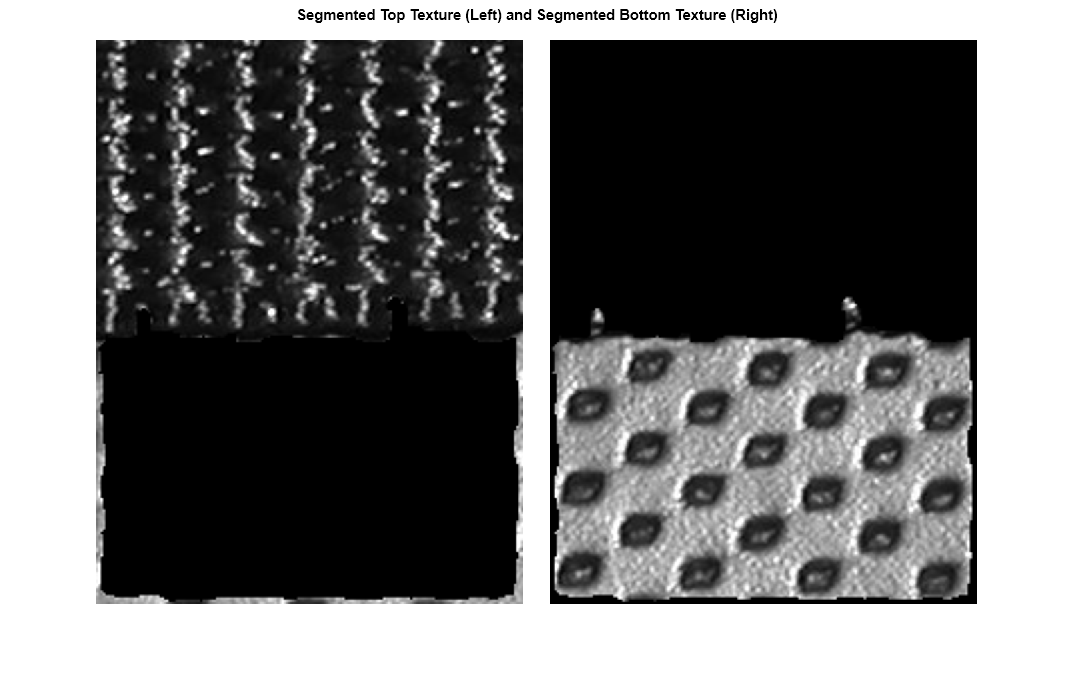
Display Segmentation Results
Create a label matrix that has the label 1 where the mask is false and the label 2 where the mask is true. Overlay label matrix on the original image.
L = mask+1;
imshow(labeloverlay(I,L))
title('Labeled Segmentation Regions')
Outline the boundary between the two textures in cyan.
boundary = bwperim(mask); imshow(labeloverlay(I,boundary,"Colormap",[0 1 1])) title('Boundary Between Textures')

See Also
entropyfilt | bwareaopen | imclose | imbinarize | imfill | bwperim | rangefilt