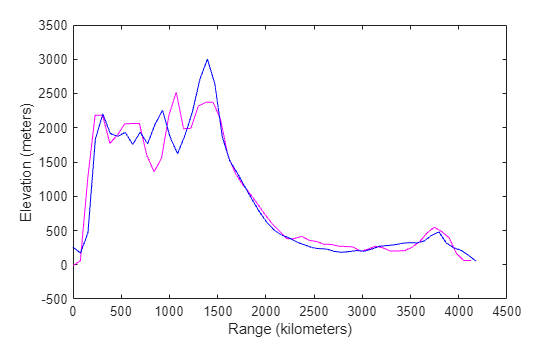
mapprofile
Interpolate between waypoints on terrain
Syntax
Description
Use Unit Sphere and Get Range in Degrees
[
interpolates intermediate points between the waypoints specified by
zq,distq,latq,lonq] = mapprofile(Z,R,lat,lon)lat and lon. You must specify the elevation
data Z and spatial reference R for the terrain.
For each intermediate point, the function returns the interpolated terrain height in
zq, the distance from the first waypoint (the
range) in distq, the latitude in
latq, and the longitude in lonq.
Specify Range Units
Specify Reference Ellipsoid
Display and Interactively Select Coordinates
mapprofile(___) displays an elevation profile of the
intermediate points in a new figure on an axesm-based map.
[___] = mapprofile enables you to interactively
select waypoints on the current axesm-based map. If the current object
on the map is a regular data grid, then the function uses the
z-coordinate data (the ZData property) as the
terrain elevation data. Otherwise, the function uses z-coordinate data
from the first regular data grid it finds on the map. If the grid does not have
z-coordinate data, then the function uses the color data (the
CData property), instead. To finish selecting points, press
Enter.