writeVideo
Write video data to file
Description
Examples
Write an RGB image to a Motion JPEG 2000 file with lossless compression.
Create an array containing data from the sample still image, peppers.png.
A = imread("peppers.png");Create a VideoWriter object for a new video file. Use the "Archival" profile to specify a Motion JPEG 2000 file with lossless compression.
v = VideoWriter("myFile","Archival");
Verify the type of video compression for the new file.
v.VideoCompressionMethod
ans = 'Motion JPEG 2000'
Open the VideoWriter object for writing and write the image data in A to the file.
open(v) writeVideo(v,A)
Close the VideoWriter object.
close(v)
Read image and colormap data from the sample indexed image file, corn.tif.
[X,map] = imread("corn.tif");Create a VideoWriter object for a new indexed AVI file.
v = VideoWriter("myIndexed.avi","Indexed AVI");
Assign the colormap data to the Colormap property of v.
v.Colormap = map;
Open the VideoWriter object for writing. After you open v, you cannot change its properties.
open(v)
Write the image data in X to the video file.
writeVideo(v,X)
Close the VideoWriter object.
close(v)
Create objects to read and write a sample video, and open the AVI file for writing.
reader = VideoReader("xylophone_video.mp4"); writer = VideoWriter("transcoded_xylophone.avi","Uncompressed AVI"); writer.FrameRate = reader.FrameRate; open(writer);
Read and write each frame.
while hasFrame(reader) img = readFrame(reader); writeVideo(writer,img) end
Clear the VideoReader object and close the VideoWriter object.
clear reader
close(writer)Set up the axes and figure properties to generate frames for the video.
Z = peaks; surf(Z); axis tight manual
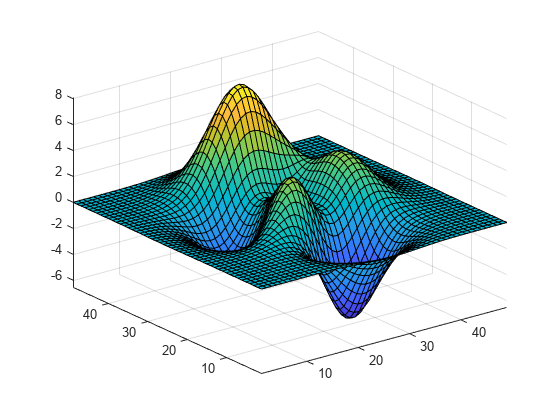
set(gca,"NextPlot","replacechildren")
Create a VideoWriter object for the output video file and open the object for writing.
v = VideoWriter("peaks.avi");
open(v)Generate a set of frames, get each frame from the figure, and then write each frame to the file.
for k = 1:20 surf(sin(2*pi*k/20)*Z,Z) frame = getframe(gcf); writeVideo(v,frame) end
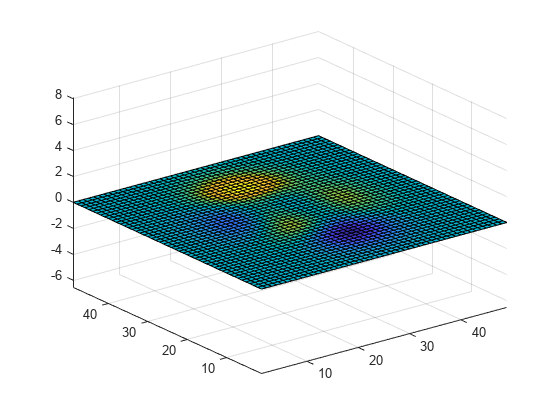
Close the VideoWriter object.
close(v)
Input Arguments
Input VideoWriter object. Use VideoWriter to create the
object.
Values representing grayscale or RGB color images, specified as a 2-D, 3-D, or 4-D array:
For a single grayscale, monochrome, or indexed image,
imgmust be two dimensional: height-by-widthFor a single truecolor (RGB) image,
imgis three dimensional: height-by-width-by-3.For a sequence of grayscale images,
imgis four dimensional:. height-by-width-by-1-by-frames. The height and width must be consistent for all frames within a file.For a sequence of RGB images,
imgis four dimensional: height-by-width-by-3-by-frames. The height and width must be consistent for all frames within a file.
When creating AVI or MPEG-4 files:
imgis an array ofsingle,double, oruint8values representing one or more grayscale or RGB color images, whichwriteVideowrites as one or more RGB video frames.Data of type
singleordoublemust be in the range[0,1], except when writing indexed AVI files.
When creating Motion JPEG 2000 files:
imgis an array ofuint8,int8,uint16, orint16values representing one or more monochrome or RGB color images.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | uint8 | uint16
Frame data, specified as a 1-by-1 structure array representing
a single frame, or a 1-by-F array of structures
representing multiple frames. Each frame contains two fields: cdata and colormap.
The frame array is typically returned by the getframe function.
If colormap is not empty, then each element
of cdata should be a 2-D (height-by-width) array.
The height and width must be consistent for all frames within a file.
colormap can contain a maximum of 256 entries.
Each element of colormap must be in the range [0,1].
When you create a VideoWriter object, the profile input
and the size of cdata determine how
writeVideo uses frame.
profile of VideoWriter object | Size of each element of cdata | Behavior of writeVideo |
|---|---|---|
| 2-D (height-by-width) | Use frame as provided. |
'Grayscale AVI' | 2-D (height-by-width) | Use frame as provided. colormap should be
empty. |
All other profiles | 2-D (height-by-width) | Construct RGB image frames using the colormap field |
| 3-D (height-by-width-by-3) | Ignore the colormap field. Construct RGB
image frames using the cdata field |
Data Types: struct
Version History
Introduced in R2010b
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)