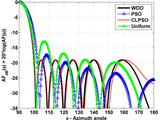
The Wind Driven Optimization (WDO) algorithm
The Wind Driven Optimization (WDO) algorithm is a new type of nature-inspired global optimization methodology based on atmospheric motion. The Wind Driven Optimization (WDO) technique is a population based iterative heuristic global optimization algorithm for multi-dimensional and multi-modal problems with the ability to implement constraints on the search domain. At its core, a population of infinitesimally small air parcels navigates over an N-dimensional search space following Newton's second law of motion, which is also used to describe the motion of air parcels within the earth's atmosphere. Compared to similar particle based algorithms, WDO employs additional terms in the velocity update equation (e.g. gravitation and Coriolis forces), providing robustness and extra degrees of freedom to fine tune the optimization. Along with the theory and terminology of WDO, a numerical study for tuning the WDO parameters is presented at the www.thewdo.com. WDO is further applied to electromagnetics optimization problems listed on the www.thewdo.com. These examples suggest that WDO can, in some cases, out-perform other well-known techniques such as Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and that WDO is well-suited for problems with both discrete and continuous-valued parameters.
Please refer to the www.thewdo.com for detailed description of the Wind Driven Optimization algorithm.
Cite As
Zikri Bayraktar (2026). The Wind Driven Optimization (WDO) algorithm (https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/44865-the-wind-driven-optimization-wdo-algorithm), MATLAB Central File Exchange. Retrieved .
MATLAB Release Compatibility
Platform Compatibility
Windows macOS LinuxCategories
- Mathematics and Optimization > Global Optimization Toolbox >
- Mathematics and Optimization > Optimization Toolbox > Nonlinear Optimization >
Tags
Discover Live Editor
Create scripts with code, output, and formatted text in a single executable document.