iqimbal
Apply I/Q imbalance to input signal
Description
Examples
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Algorithms
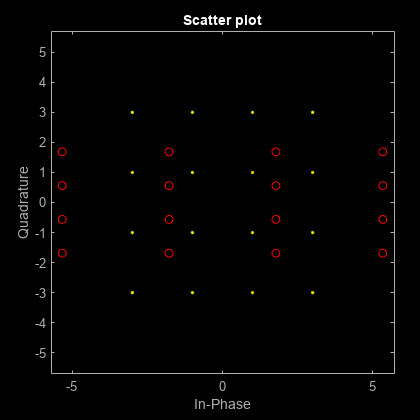
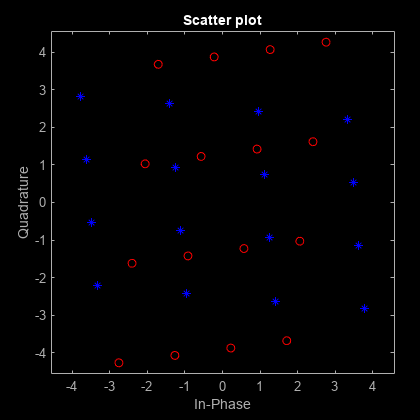
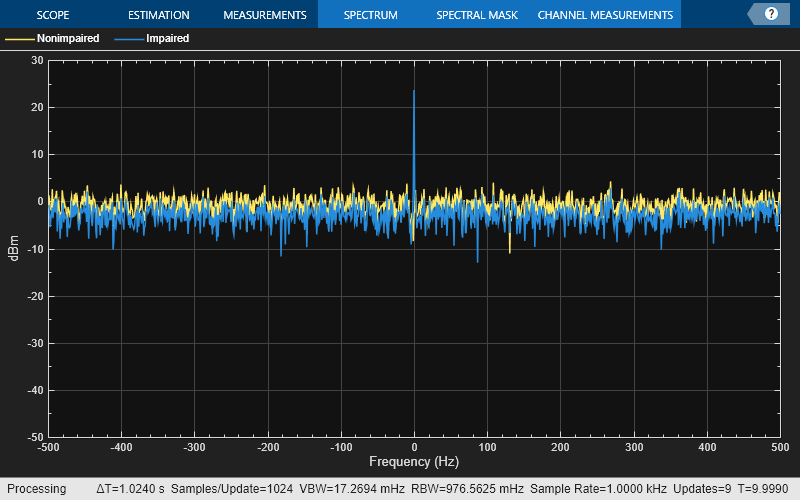
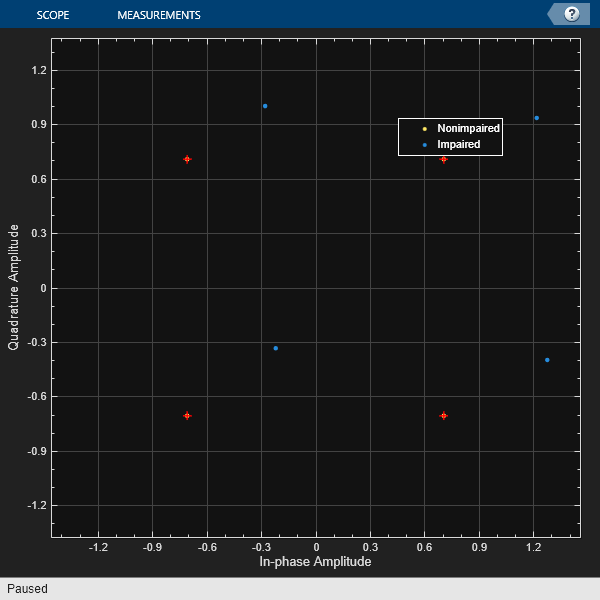
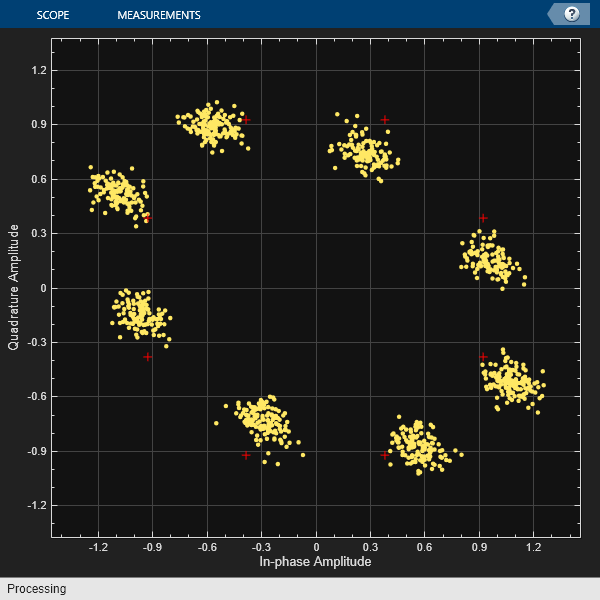
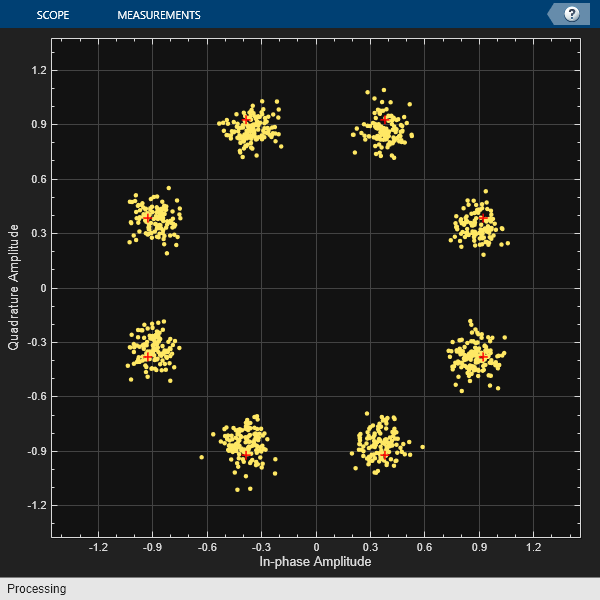
The iqimbal function applies
an I/Q amplitude and phase imbalance to an input signal.
Given amplitude imbalance Ia in dB, the gain, g, resulting from the imbalance is defined as
Applying the I/Q imbalance to input signal x results in output signal y such that
where g is the imbalance gain and Ip is the phase imbalance in degrees.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2016b
See Also
iqcoef2imbal | iqimbal2coef | comm.IQImbalanceCompensator | I/Q Imbalance