uitab
Create tabbed panel
Description
t = uitab creates a tab inside a tab group and returns the
Tab object. If there is no tab group available, MATLAB® calls the figure function to create a figure.
Then it creates a tab group in that figure and places the tab inside the tab
group.
t = uitab( creates the tab in the
specified parent container. The parent container must be a tab group. For more
information, see Name-Value Arguments.parent)
t = uitab(___,
creates a tab with properties specified by one or more name-value arguments. For
example, specify the tab title using the Name,Value)Title property. Use this
option with any of the input argument combinations in the previous syntaxes.
Examples
Create a tab group with two tabs in a UI figure. Specify the title of each of the tabs.
fig = uifigure; tg = uitabgroup(fig); t1 = uitab(tg,"Title","Data"); t2 = uitab(tg,"Title","Plots");

Create a tab group with two tabs in a UI figure, and customize the appearance of the tabs by specifying property values.
fig = uifigure; tg = uitabgroup(fig); t1 = uitab(tg,"Title","Data","BackgroundColor",[0 0.4470 0.7410]); t2 = uitab(tg,"Title","Plots","BackgroundColor",[0 0.4470 0.7410]);

Query the text color of the Data tab title.
c = t1.ForegroundColor
c = 1×3
0.1294 0.1294 0.1294
Update the text color to match the tab background color.
t1.ForegroundColor = t1.BackgroundColor;

Create a tab group containing one tab. Add six UI components to the tab, with the first three lying outside the upper border of the tab.
fig = uifigure; tg = uitabgroup(fig,'Position',[20 20 196 145]); t = uitab(tg,'Title','Member Information'); ef1 = uieditfield(t,'text','Position',[11 165 140 22],'Value','First Name'); ef2 = uieditfield(t,'text','Position',[11 140 140 22],'Value','Last Name'); ef3 = uieditfield(t,'text','Position',[11 115 140 22],'Value','Address'); dd = uidropdown(t,'Position',[11 90 140 22],'Items',{'Male','Female'}); cb = uicheckbox(t,'Position',[11 65 140 22],'Text','Member'); b = uibutton(t,'Position',[11 40 140 22],'Text','Send');
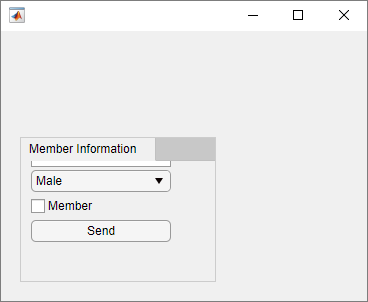
Enable scrolling by setting the Scrollable property
of the tab to 'on'. By default, the scroll box displays
at the top.
t.Scrollable = 'on';
In a new script, create a tab group with two tabs in a UI figure. Specify the
SelectionChangedFcn property as a handle to a function named
displaySelection. This function executes when a user switches
between tabs in the tab group.
At the bottom of the script, define the displaySelection
function to accept the two input arguments that MATLAB passes to callback functions:
src— The component that executed the callbackevent— Information about the user interaction that triggered the callback
In the callback function, write code to display the title of the visible tab in the Command Window.
fig = uifigure; tg = uitabgroup(fig,"SelectionChangedFcn",@displaySelection); t1 = uitab(tg,"Title","Data"); t2 = uitab(tg,"Title","Plots"); function displaySelection(src,event) t = event.NewValue; title = t.Title; disp("Viewing the " + title + " tab") end
Run the script and toggle between tabs to display the tab titles.
For more information, see Create Callbacks for Apps Created Programmatically.
Input Arguments
Parent container, specified as a TabGroup
object.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: uitab(Title="Options") specifies that the tab title is
Options.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: uitab("Title","Options") specifies that the tab title
is Options.
Note
The properties listed here are a subset of the available properties. For the
full list, see Tab.
Title, specified as a character vector, string scalar, or categorical array. If you specify this property as a categorical array, MATLAB displays only the first element in the array.
MATLAB does not interpret a vertical slash ('|') character as
a line break, it displays as a vertical slash in the title.
If you want to specify a Unicode® character, pass the Unicode decimal
code to the char function.
For example, ['Multiples of ' char(960)] displays
as Multiples of π.
Background color, specified as an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, or one of the color options listed in the table.
RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes are useful for specifying custom colors.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1]; for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a character vector or a string scalar that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Thus, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan"
| "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
This table lists the default color palettes for plots in the light and dark themes.
| Palette | Palette Colors |
|---|---|
Before R2025a: Most plots use these colors by default. |
|
|
|
You can get the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for these palettes using the orderedcolors and rgb2hex functions. For example, get the RGB triplets for the "gem" palette and convert them to hexadecimal color codes.
RGB = orderedcolors("gem");
H = rgb2hex(RGB);Before R2023b: Get the RGB triplets using RGB =
get(groot,"FactoryAxesColorOrder").
Before R2024a: Get the hexadecimal color codes using H =
compose("#%02X%02X%02X",round(RGB*255)).
This property is read-only.
Location and size of the tab, returned as a four-element vector
of the form [left bottom width height]. This table
describes each element in the vector.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
left | Distance from the inner left edge of the tab group to the inner left edge of the tab |
bottom | Distance from the inner bottom edge of the tab group to the inner bottom edge of the tab |
width | Distance between the right and left inner edges of the tab |
height | Distance between the top and bottom inner edges of the tab |
All measurements are in units specified by the Units property.
Note
These are some important points to consider when using the Position property:
Positionvalues are affected by the length of the tab title and theTabLocationproperty of the parentTabGroupobject.Positionvalues are relative to the drawable area of the parentTabGroup, which is the area inside its borders.If the tab is in a grid layout manager, the value of the
Positionproperty is not immediately updated. To use thePositionvalue to resize the tab children relative to the tab size, use aSizeChangedFcncallback.
Units of measurement, specified as one of the values in this table.
| Units Value | Description |
|---|---|
'pixels' (default in uifigure-based apps) | On Windows® and Macintosh systems, the size of a pixel is 1/96th of an inch. This size is independent of your system resolution. On Linux® systems, the size of a pixel is determined by your system resolution. |
'normalized' (default in figure-based apps) | These units are normalized with respect to the parent container. The lower-left corner of the container maps to |
'inches' | Inches. |
'centimeters' | Centimeters. |
'points' | Points. One point equals 1/72nd of an inch. |
'characters' | These units are based on the default uicontrol font of the graphics root object:
To access the default uicontrol font, use |
The recommended value is 'pixels', because most MATLAB app building functionality measures distances in pixels. You can create an
object that rescales based on the size of the parent container by parenting the object
to a grid layout manager created using the uigridlayout function. For more information, see Lay Out Apps Programmatically.
Version History
Introduced in R2014bThese properties are available for tabs in apps created using the
figure function:
ScrollableAutoResizeChildren
For apps created using the figure function, when you query the
InnerPosition property of a tab group, the property returns a
different value than in the previous release. In addition, if the
TabLocation is 'left' or
'bottom', when you query the Position,
InnerPosition, and OuterPosition
properties of a tab in the tab group, the properties might return different values
than in the previous release. These changes make the property values and behaviors
consistent with the properties in uifigure-based apps.
This table describes the differences in the property values between R2025a and previous releases.
| Property | Starting in R2025a | R2024b and Earlier | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Image | Description | Image | |
InnerPosition of a tab group | A four-element vector of the form [left bottom width
height] that represents the size and location of the
tab group relative to the drawable area of its parent,
excluding borders and titles of the tabs it
contains | Tab group
| A four-element vector of the form [left bottom width
height] that represents the size and location of the
tab group relative to the drawable area of its parent,
including borders and titles of the tabs it
contains | Tab group
|
Position, InnerPosition,
and OuterPosition of a tab | A four-element vector of the form [left bottom width
height] that represents the size and location of the
tab relative to the tab group drawable area, where the tab group
drawable area excludes borders
and titles | Tab
| A four-element vector of the form [left bottom width
height] that represents the size and location of the
tab relative to the tab group drawable area, where the tab group
drawable area includes borders
and titles | Tab
|
If you notice changes in your app layout, consider updating your code in this way:
Tab group
InnerPosition— Replace references to the tab groupInnerPositionproperty with the tab groupPositionproperty to use the size and location of the tab group including the borders and tab titles.Tab
Position,InnerPosition, andOuterPosition— Replace references to the first two elements of the position vector to instead use the space taken up on the left or bottom by the tab titles. For example, if your app contains a tab group with aTabLocationvalue of'left'and you reference thePositionproperty of a tab in that tab group, replace that reference with the horizontal distance between the tab group border and the tab drawable area.
For apps created in App Designer and using the uifigure
function, when you query the InnerPosition property of a tab
group, the property returns a different value than in the previous release. In
addition, if the TabLocation is 'left' or
'bottom', when you query the Position,
InnerPosition, and OuterPosition
properties of a tab in the tab group, the properties might return different values
than in the previous release.
This table describes the differences in the property values between R2022b and previous releases.
| Property | Starting in R2022b | R2022a and Earlier | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Image | Description | Image | |
InnerPosition of a tab group | A four-element vector of the form [left bottom width
height] that represents the size and location of the
tab group relative to the drawable area of its parent,
excluding borders and titles of the tabs it
contains | Tab group
| A four-element vector of the form [left bottom width
height] that represents the size and location of the
tab group relative to the drawable area of its parent,
including borders and titles of the tabs it
contains | Tab group
|
Position, InnerPosition,
and OuterPosition of a tab | A four-element vector of the form [left bottom width
height] that represents the size and location of the
tab relative to the tab group drawable area, where the tab group
drawable area excludes borders
and titles | Tab
| A four-element vector of the form [left bottom width
height] that represents the size and location of the
tab relative to the tab group drawable area, where the tab group
drawable area includes borders
and titles | Tab
|
If you notice changes in your app layout, consider updating your code in this way:
Tab group
InnerPosition— Replace references to the tab groupInnerPositionproperty with the tab groupPositionproperty to use the size and location of the tab group including the borders and tab titles.Tab
Position,InnerPosition, andOuterPosition— Replace references to the first two elements of the position vector to instead use the space taken up on the left or bottom by the tab titles. For example, if your app contains a tab group with aTabLocationvalue of'left'and you reference thePositionproperty of a tab in that tab group, replace that reference with the horizontal distance between the tab group border and the tab drawable area.
Starting in R2020a, using the UIContextMenu property to
assign a context menu to a graphics object or UI component is not recommended. Use
the ContextMenu property instead. The property values are the
same.
There are no plans to remove support for the UIContextMenu
property at this time. However, the UIContextMenu property no
longer appears in the list returned by calling the get function
on a graphics object or UI component.
Starting in R2018b, using the TooltipString property to
specify a tooltip for a UI component is not recommended. Use the
Tooltip property instead. The property values are the
same.
There are no plans to remove support for the TooltipString
property at this time. However, the TooltipString property no
longer appears in the list returned by calling the get function
on a UI component.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)



