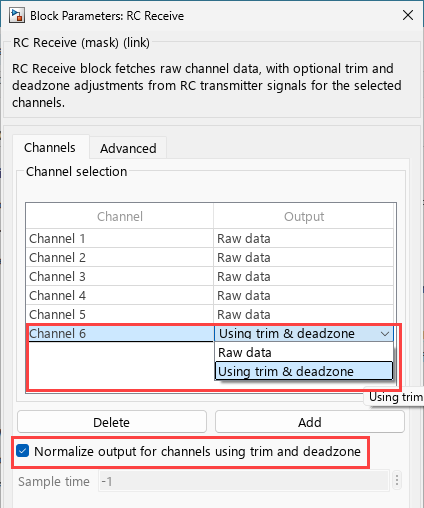
RC Receive
Add-On Required: This feature requires the UAV Toolbox Support Package for ArduPilot® Autopilots add-on.
Libraries:
UAV Toolbox Support Package for ArduPilot Autopilots /
Peripheral Blocks
Description
The RC Receive block acquires raw input data from selected channels of an RC transmitter. The block provides options to apply trim and deadzone adjustments for output normalization. Additionally, the block can output auxiliary information such as flight mode, radio signal strength indicator (RSSI), arming status, and motor emergency stop status.
Examples
Verify RC Transmitter Input with RC Receive Block
Test your RC transmitter with the RC Receive block in Simulink.
Limitations
This block is not supported in triggered subsystems.
Ports
Output
The RC Receive block outputs the failsafe status by default. If the RC
transmitter turns off or loses signal during operation, the failsafe output
switches to 1. Use this output to trigger safety mechanisms
in your model.
Data Types: double
Raw data for each selected channel. When you enable normalization, it adjusts the output values using the specified trim and deadzone settings.
Data Types: double
The block outputs the flight mode index (starting from 0) based on your Mission Planner configuration. This value indicates the current mapped flight mode.
Dependencies
To enable this port, select the Output flight mode parameter.
Data Types: uint8
The block outputs the radio signal strength from the RC transmitter. Use this value in your model for monitoring or implementing safety mechanisms.
Dependencies
To enable this port, select the Output radio signal strength indicator(RSSI) parameter.
Data Types: int32
The block outputs 1 when armed, 0 when
disarmed.
Dependencies
To enable this port, select the Output arming status parameter.
Data Types: uint8
The block outputs a signal that indicates whether the motor emergency stop has been triggered.
Dependencies
To enable this port, select the Output motor emergency stop status parameter.
Data Types: uint8
Parameters
Channels tab
Select which RC channels you want to read from your transmitter. Add or remove
channels using the interface. The block displays Ch
outputs based on your selections
in this parameter list. You can add a maximum of x Raw16
channels.
Select this parameter to normalize the outputs for the selected channels using the specified trim and deadzone settings.
The time interval at which the block retrieves values from the ArduPilot autopilot.
Advanced tab
Select this parameter to enable the Port output port . To view information on the mapping of flight modes to channel values, see Flight Mode Mapping.
Select this parameter to enable the RSSI output port .
Select this parameter to enable the Arm output port .
Select this parameter to enable the Estop output port.
More About
ArduPilot supports a wide range of flight modes, each designed to provide specific control characteristics and automation features for different flight scenarios. The following tables outline the mapping between flight mode values and their corresponding meanings for both Plane and Copter firmware.
The table below lists the available flight modes for ArduPilot Plane, along with their associated numeric values and descriptions:
Mapping Table - Plane
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
0 | Manual |
1 | CIRCLE |
2 | STABILIZE |
3 | TRAINING |
4 | ACRO |
5 | FBWA |
6 | FBWB |
7 | CRUISE |
8 | AUTOTUNE |
10 | Auto |
11 | RTL |
12 | Loiter |
13 | TAKEOFF |
14 | AVOID_ADSB |
15 | Guided |
17 | QSTABILIZE |
18 | QHOVER |
19 | QLOITER |
20 | QLAND |
21 | QRTL |
22 | QAUTOTUNE |
23 | QACRO |
24 | THERMAL |
25 | Loiter to QLand |
The following table shows the flight mode mapping for ArduPilot Copter, indicating each mode’s numeric value and its meaning.
Mapping Table - Copter
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
0 | Stabilize |
1 | Acro |
2 | AltHold |
3 | Auto |
4 | Guided |
5 | Loiter |
6 | RTL |
7 | Circle |
9 | Land |
11 | Drift |
13 | Sport |
14 | Flip |
15 | AutoTune |
16 | PosHold |
17 | Brake |
18 | Throw |
19 | Avoid_ADSB |
20 | Guided_NoGPS |
21 | Smart_RTL |
22 | FlowHold |
23 | Follow |
24 | ZigZag |
25 | SystemID |
26 | Heli_Autorotate |
27 | Auto RTL |
28 | Turtle |
When you select Using trim & deadzone as the output
for a channel in the RC Receive block, the output is normalized based on the RC
channel's trim and deadzone settings.
Key Parameters
Here are the parameters used in the normalization calculation:
Key Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
radio_in | The raw input value from the RC transmitter for the channel. |
radio_trim | The trim (center) value of the RC channel. Set via the parameter
RCx_TRIM (where x = 1 to 16). |
dead_zone | The deadzone value, set via parameter RCx_DZ (e.g.,
RC1_DZ), which defines the range around the trim where
small movements are ignored. |
radio_min | The minimum value for the RC channel. |
radio_max | The maximum value for the RC channel. |
reversed | Boolean indicating if the channel is reversed. If the channel is reversed, this is true. |
reverse_mul | Multiplier, set to -1 if reversed, otherwise 1. |
Step-by-Step Calculation
The calculation proceeds as follows:
Define Deadzone Boundaries:
dz_min = radio_trim - dead_zone dz_max = radio_trim + dead_zone
Any input between
dz_minanddz_maxis considered "neutral" (output = 0).
Determine Output Based on Input:
Below Deadzone: If
radio_in < dz_minanddz_min > radio_minoutput = reverse_mul * (radio_in - dz_min) / (dz_min - radio_min)
Above Deadzone: If
radio_in > dz_maxandradio_max > dz_maxoutput = reverse_mul * (radio_in - dz_max) / (radio_max - dz_max)
Within Deadzone:
output = 0
Reverse Direction (if applicable):
If the channel is reversed,
reverse_mul = -1, otherwisereverse_mul = 1.
Constrain Output:
The output is constrained to the range [-1.0, 1.0]:
output = constrain_float(output, -1.0, 1.0)
If the value is more
1, then it is1and if the output is less than-1, it is-1.
What Happens When Not Normalized?
When Normalize output for channels using trim and deadzone option is not selected then the RC channel values are not adjusted for trim or deadzone and the formula is calculated using this formula:
trimDzChannelData = static_cast<int16_T>(minChVal + (normTrimDz + 1) * (maxChVal - minChVal) / 2);
This formula is used to convert the normalized RC channel value (which ranges from
-1 to 1) back to the actual channel value range
defined by the hardware (from minChVal to
maxChVal).
normTrimDz: This is the normalized value (from
-1to1) obtained from the previous calculation (see the earlier code block).minChVal and maxChVal: These are the minimum and maximum possible values for the channel (for example,
1000and2000for many RC systems).
This converts a normalized value (from -1 to 1)
back to the original PWM range.
When
normTrimDz=-1, the output isminChVal.When
normTrimDz=1, the output ismaxChVal.Values in between are linearly interpolated.
Version History
Introduced in R2025b
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)