horn
Create regular or AI-based horn antenna
Description
The default horn object is a pyramidal horn antenna
resonating around 15.86 GHz with a standard-gain of around 15.6 dBi. The default horn
antenna operates in the X-Ku band, which ranges from 10 GHz to 16 GHz. By default, the
horn antenna feed is a WR-75 rectangular waveguide with an operating frequency at 7.87
GHz.
For a given flare angles of the horn and dimensions of the waveguide, use the
hornangle2size utility function to
calculate the equivalent flare width and flare height of the horn.
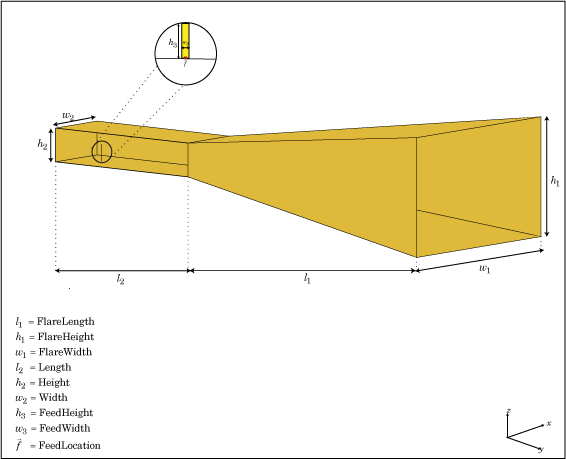
You can perform full-wave EM solver based analysis on the regular
horn antenna or you can create a
horn type AIAntenna and explore the design
space to tune the antenna for your application using AI-based analysis.
Creation
Description
h = horn
h = horn(PropertyName=Value)PorpertyName is the property name
and Value is the corresponding value. You can specify
several name-value arguments in any order as
PropertyName1=Value1,...,PropertyNameN=ValueN.
Properties that you do not specify, retain their default values.
For example, h = horn(FlareLength=0.2) creates a
standard-gain pyramidal horn antenna with flare length of 0.2 m. and default
values for other properties.
You can also create a regular
hornantenna resonating at a desired frequency using thedesignfunction. For example, to create a regularhornantenna resonating at 12 GHz, use the following syntax:To analyze this antenna use object functions of the>> design(horn,12e9)
horn. Use this workflow to design, tune, and analyze ahornantenna using conventional full-wave solvers.You can create an AI-based
hornantenna resonating at a desired frequency using thedesignfunction. Using AI-based antenna models over conventional full-wave solvers significantly reduces the simulation time required to fine-tune the antenna to meet your design goals. Set theForAIargument in thedesignfunction totrueto create ahorntypeAIAntennaobject. To use this feature, you need license to the Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox™ in addition to the Antenna Toolbox™. For example, to create an AI-basedhornantenna resonating at 12 GHz, use the following syntax:The AI-based>> design(horn,12e9,ForAI=true)
hornantenna retains the Width, Height, FlareLength, FlareHeight, and FeedHeight properties of the regularhornantenna as tunable properties. Rest of the properties of the regularhornantenna are converted into read-only properties in its AI-based version. To find the upper and lower bounds of the tunable properties, use thetunableRangesfunction.To analyze this antenna use object functions of the
AIAntenna. Use this workflow to design, tune, and analyze ahornantenna using its AI-based model. To create a regularhornantenna from this AI-based antenna, use theexportAntennafunction.
Properties
Object Functions
axialRatio | Calculate and plot axial ratio of antenna or array |
bandwidth | Calculate and plot absolute bandwidth of antenna or array |
beamwidth | Beamwidth of antenna |
charge | Charge distribution on antenna or array surface |
current | Current distribution on antenna or array surface |
design | Create antenna, array, or AI-based antenna resonating at specified frequency |
efficiency | Calculate and plot radiation efficiency of antenna or array |
EHfields | Electric and magnetic fields of antennas or embedded electric and magnetic fields of antenna element in arrays |
impedance | Calculate and plot input impedance of antenna or scan impedance of array |
info | Display information about antenna, array, or platform |
memoryEstimate | Estimate memory required to solve antenna or array mesh |
mesh | Generate and view mesh for antennas, arrays, and custom shapes |
meshconfig | Change meshing mode of antenna, array, custom antenna, custom array, or custom geometry |
optimize | Optimize antenna and array catalog elements using SADEA or TR-SADEA algorithm |
pattern | Plot radiation pattern of antenna, array, or embedded element of array |
patternAzimuth | Azimuth plane radiation pattern of antenna or array |
patternElevation | Elevation plane radiation pattern of antenna or array |
peakRadiation | Calculate and mark maximum radiation points of antenna or array on radiation pattern |
rcs | Calculate and plot monostatic and bistatic radar cross section (RCS) of platform, antenna, or array |
resonantFrequency | Calculate and plot resonant frequency of antenna |
returnLoss | Calculate and plot return loss of antenna or scan return loss of array |
show | Display antenna, array structures, shapes, or platform |
sparameters | Calculate S-parameters for antenna or array |
vswr | Calculate and plot voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR) of antenna or array element |
Examples
References
[1] Balanis, Constantine A.Antenna Theory. Analysis and Design. 3rd Ed. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 2005.
